Project Scheduling
- b00130630
- Nov 7, 2021
- 3 min read
Updated: Nov 30, 2021

Figure 1: Project Schedule on MS Office
This blog examines project scheduling and the relationship between different tasks within the project.
The schedule is the conversion of a project action plan into an operating timetable. It is a monitoring and controlling aid for the entire project.
A schedule can be displayed as network of activity and event relationships between all the various inputs, known as a network diagram (See Figure 1). Tasks that must precede or follow other tasks are then clearly identified as are the dependencies between different tasks. This shows how the tasks will affect the overall project duration is delayed.
The two most common networking techniques are PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method). The techniques two are quite similar and are interchangeable.
Terminology
Here are some terms used in project scheduling:
Activity: A specific task or set of tasks required by the project.
Event : The result of completing an activity. It is an end state occurring at a particular time and uses no resources.
Network: The combination of all activities and events that define the project and the activity precedence relationships.
Path: The series of connected activities (or intermediate events) between any two events in a network.
Critical: Activities, events, or paths which, if delayed, will delay the completion of the project. A project’s critical path is the sequence of critical activities that connect the project’s start event to its finish event.
An activity may have a successor, but no predecessor, in which case it starts a network. It may have a predecessor, but no successor, in which case it ends a network. Or it may have both predecessors and successors in which case it is in the middle of a network.
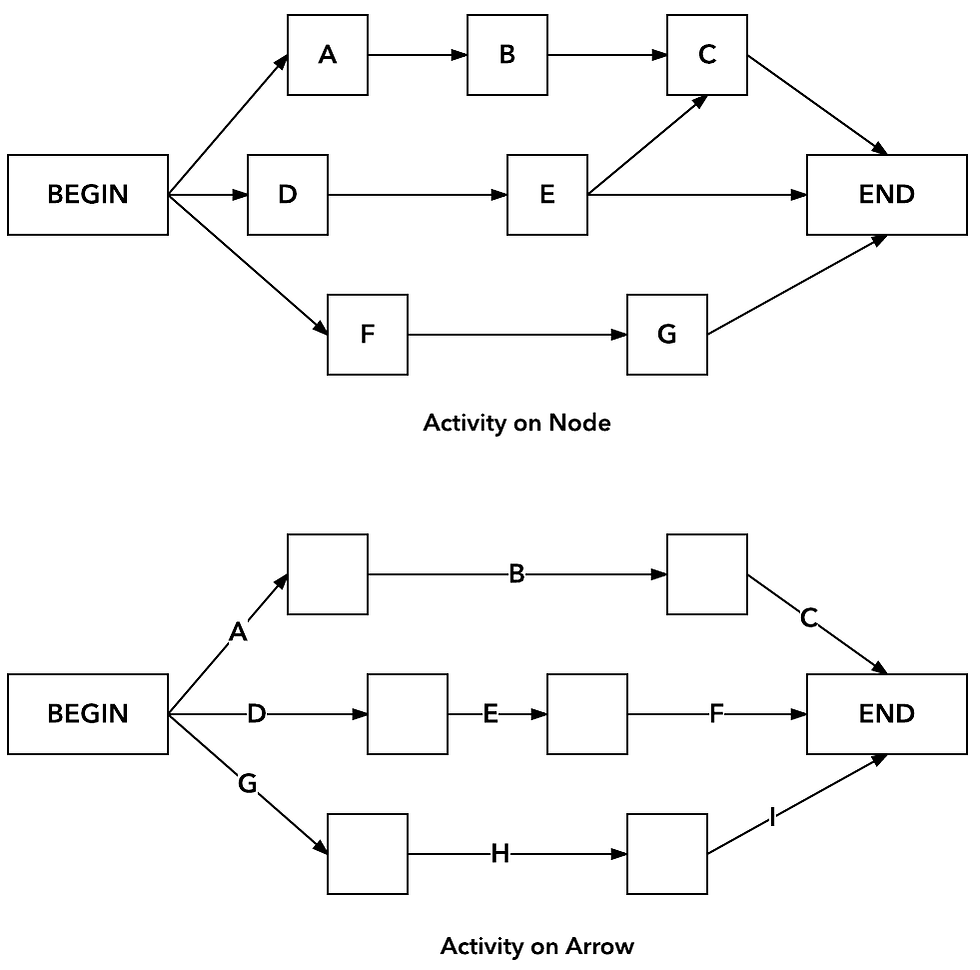
Figure 2: Activity on Node and Activity on Arrow
There are two main networks used to display activities (See Figure 2):
Activity on Nodes (AON): networks use nodes to represent activities with arrows to show precedence relationships
Activity on Arrow (AOA): networks use arrows to represent activities while nodes/boxes stand for events
The AON networks are easier to draw and they are the type used in MS Project.
Each node on the Gantt Chart includes certain additional information required for that node such as activity name, the duration, the Earliest Start Time (EST), Earliest Finish Time (EFT), Latest Start Time (LST) and Latest Finish Time (LFT).

Figure 3: Critical Path Method
Critical Path Method
The critical path for a project is the series of activities that determines the earliest time by which the project can be completed. The Critical Path Method is a network analysis technique used to predict total project duration. A critical path for a project is the longest path through the network diagram and has the least amount of float. The critical path in Figure 5, is the path outlined in red and this project is scheduled to take 54 days to complete. A good project network diagram will help to develop a more accurate critical path.

Figure 4: Forward and Backward Pass Calculation
Forward Pass Critical Path
To calculate the Earliest Start Time for an activity, sum the durations of the predecessor tasks. To calculate the Earliest Finish Time, add the duration of the activity to the Earliest Start Time. Do this for all tasks to estimate the Earliest Finish Time for the Project. The longest time path is the critical path. This is called the forward pass method to establish the critical path method and it moves from left to right across the network diagram.

Figure 5: A Different Kind of Backward Pass
Backward Pass
The backward pass is a method to ensure deadlines are met. It calculates the latest start time and latest finish time for each activity within the critical path, starting with the finishing time for a task and subtracting the duration. This identifies if there is 'slack' time for any task and lets the project manager know if resources should be reallocated.



Hi Elaine! You explain a difficult topic very clearly and you make it easy to understand. Good work! Michaela
Really good blog, great use of visual aids to assist with understanding the topic, well done! Kerry